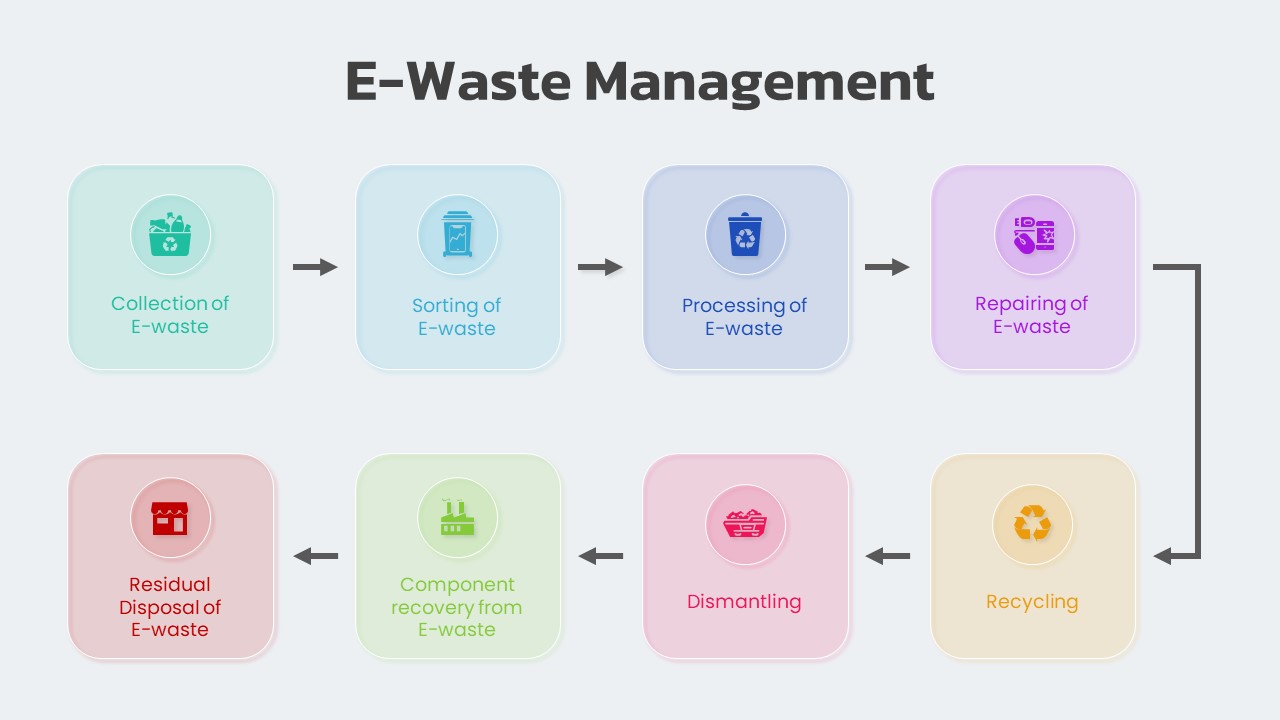
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) for e-waste refers to the legal obligation placed on manufacturers of electrical or electronic equipment to manage the collection, recycling, and environmentally responsible disposal of e-waste generated from their products.

Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is a key element of waste management, focused on ensuring the responsible disposal of electronic devices that are no longer useful to consumers. It involves establishing a reverse collection system and recycling post-consumer waste to create an efficient e-waste disposal solution for end-of-life products.
Under the e-Waste Management Rules and the Amendment Rules manufacturers, producers, importers, and bulk consumers of electrical and electronic equipment must meet annual targets to fulfill their EPR responsibilities. To obtain EPR authorization from the Central Pollution Control Board, companies are required to submit an EPR plan that outlines how they will collect, recycle, and manage their end-of-life products in compliance with EPR regulations to meet their yearly targets.
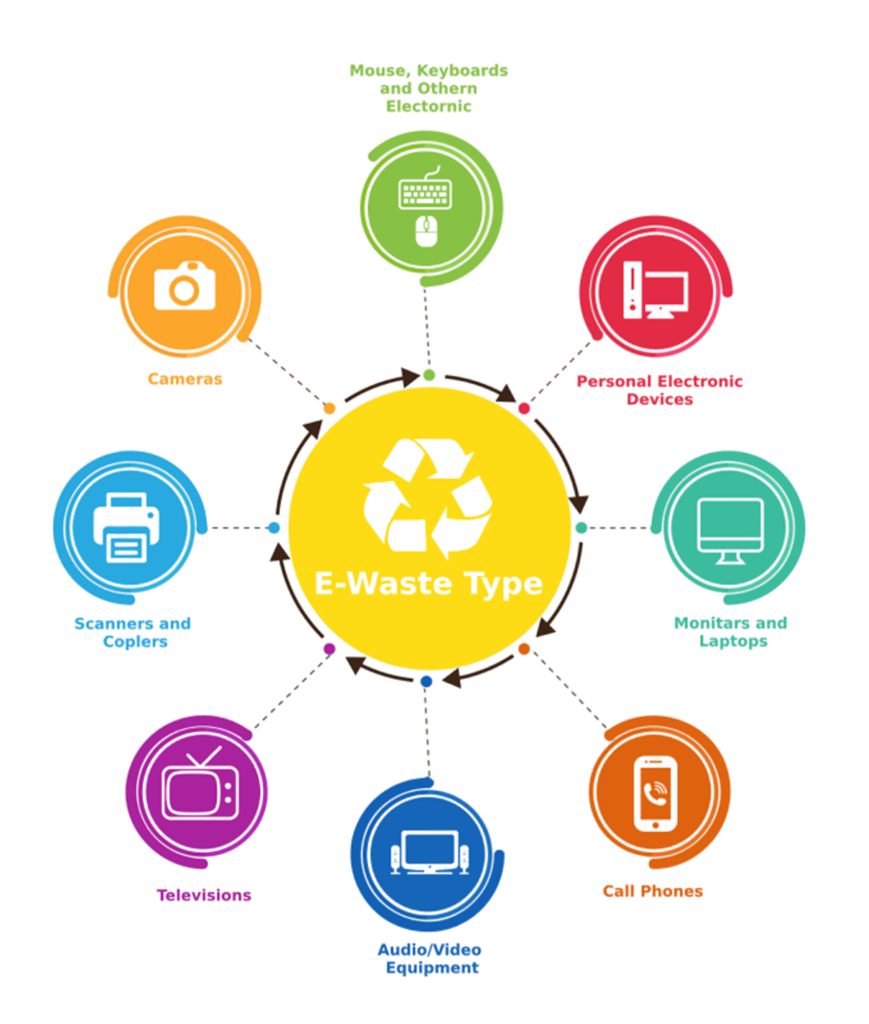
To facilitate the effective implementation of EPR, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Government of India, has issued guidelines for Extended Producer Responsibility for Electronic and Electrical Waste. These guidelines were incorporated into the Third Amendment of the e-Waste Management Rules in November to enhance e-waste recycling solutions. According to these guidelines, manufacturers, producers, importers, and bulk consumers are required to register through an online centralized portal developed by the Central Pollution Control Board. This system aims to improve accountability, traceability, and transparency in meeting EPR obligations.
In summary, EPR is a vital component of waste management, and top e-waste recycling companies in India within the electrical and electronic equipment sector must take it seriously to ensure sustainable business practices and protect the environment.